Endometrial Hyperplasia: Meaning, Types, Symptoms, Causes & Treatment
Endometrial Hyperplasia is an abnormal proliferation of endometrium or endometrial glands. The abnormality arises due to estrogenic stimulation and progesterone deficiency. Endometrial Hyperplasia eventually leads to endometrial carcinoma. To prevent the development of endometrial malignancy in women, signs or symptoms must be observed for Endometrial Hyperplasia.
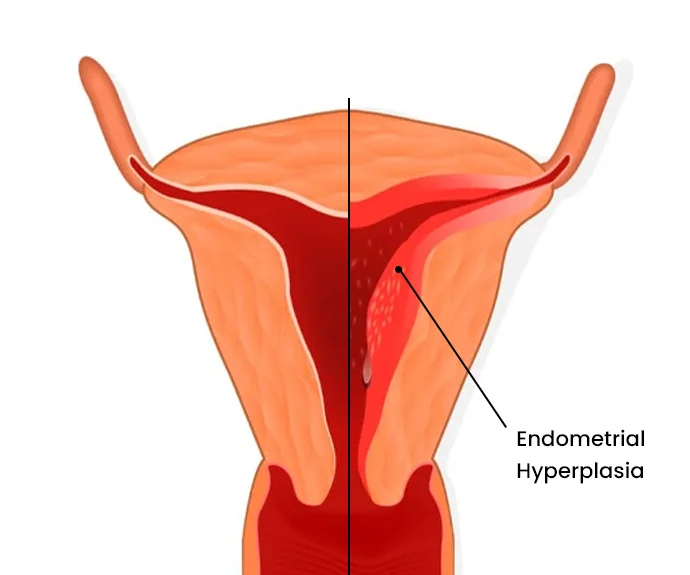
WHAT IS ENDOMETRIAL HYPERPLASIA
Endometrial hyperplasia is a condition in which the lining of the uterus, called the endometrium, becomes thicker than normal due to an increase in the number of cells. This condition can occur in women of all ages, but it is most common in women who are approaching menopause. Endometrial hyperplasia is caused by an overgrowth of cells in the lining of the uterus. This can occur for several reasons, including:
Hormonal imbalances: An increase in the hormone estrogen can cause the endometrium to thicken, leading to hyperplasia.
Obesity: Excess body weight can lead to an increase in estrogen levels, which can contribute to the development of endometrial hyperplasia.
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS): Women with PCOS have hormonal imbalances that can increase their risk of developing endometrial hyperplasia.

TYPES OF ENDOMETRIAL HYPERPLASIA
Simple Hyperplasia
This type of hyperplasia occurs when the cells in the endometrium begin to grow more than normal, but they remain normal in appearance and do not show any signs of abnormal growth or changes.
1
Complex Hyperplasia
In this type of hyperplasia, the cells in the endometrium become abnormal in appearance, with some cells growing larger and more irregularly shaped than normal.
2
Atypical Hyperplasia
This is the most severe form of hyperplasia, where the cells in the endometrium become highly abnormal and can potentially become cancerous.
3
CAUSES
- Estrogen predominance
- Progesterone insufficiency
- Perimenopause
- Exogenous causes
- Obesity
- Estrogen secreting tumors of ovaries
- Estrogen therapy
- HRT (Hormone replacement therapy)
- Tamoxifen (for treatment of breast cancer)
SYMPTOMS
- Abnormal bleeding from uterine
- Altered pattern of the menstrual cycle
- Passage of blood clots
- The foul smell of the vaginal discharge
- Blood stains with the vaginal discharge

DIAGNOSIS
The PAP smear test
Transvaginal ultrasound
Hysteroscopy
Histological examination of endometrial tissue
DO's
DONT's
TREATMENTS
NON SURGICAL TREATMENTS
- Progestin Therapy: Progestin is a hormone therapy that can help regulate the growth of the endometrium. This is a common first-line treatment for endometrial hyperplasia, especially for those with simple or complex hyperplasia without atypia. Progestin therapy can be administered in various forms, such as pills, injections, intrauterine devices (IUDs), or vaginal creams.
- Combination Hormone Therapy: Combination hormone therapy with estrogen and progestin may be recommended in some cases, such as in postmenopausal women with endometrial hyperplasia.
- Aromatase Inhibitors: Aromatase inhibitors are medications that reduce the body's production of estrogen. These may be used in women with endometrial hyperplasia caused by estrogen-producing tumors or disorders.
- Monitoring: In some cases, regular monitoring and surveillance may be recommended, especially for women with simple or complex hyperplasia without atypia.
SURGICAL TREATMENTS
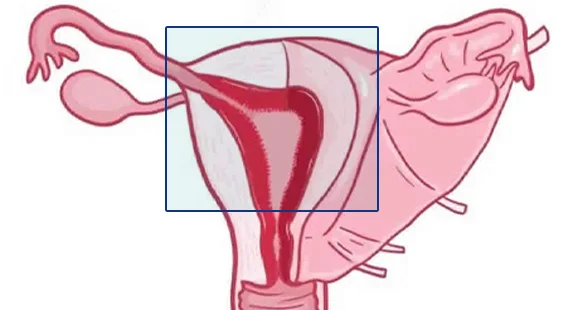
- Hysterectomy: Hysterectomy is the surgical removal of the uterus and is usually recommended for women with atypical hyperplasia, especially for those who have completed their family planning or who are postmenopausal. Hysterectomy is also considered for women who are not responding to other treatments or who have severe symptoms.
- Endometrial Ablation: Endometrial ablation is a minimally invasive procedure in which the lining of the uterus is destroyed or removed to treat endometrial hyperplasia. This procedure is recommended for women who wish to preserve their uterus or who are not good candidates for hysterectomy.
- Dilation and Curettage (D&C): D&C is a surgical procedure in which the lining of the uterus is removed by scraping it with a small instrument. This procedure is usually done under general anesthesia and may be recommended for women with non-atypical hyperplasia or who have not responded to other treatments.
- Hysteroscopy: Hysteroscopy is a minimally invasive procedure in which a small camera is inserted through the cervix to view the inside of the uterus. This procedure may be used to diagnose and treat endometrial hyperplasia.
Risk and Complications
1. Age
2. Obesity
3. Genetic
4. Diabetes Mellitus
5. Anovulatory cycles
6. PCOS
7. Ovarian cancer or tumor
8. HRT (Hormone replacement therapy)
9. Immunosuppression (in the case of individuals who get renal graft )
10. Infection

IF LEFT UNTREATED
Following complication may arise if endometrial hyperplasia is left untreated:
1. Endometrial adenocarcinoma is the most clinically significant complication arising from untreated endometrial hyperplasia.
2. Atypia endometrial hyperplasia has a greater risk of tumor development that is highly invasive if not treated properly.
COST
The average cost of laparoscopic hysterectomy to treat adenomyosis is ₹35,000 - ₹40,000. The cost varies from the type of surgical procedure, hospital facilities and cities.
Financial Options

INSURANCE COVERAGE
The cost of surgical treatment for endometrial hyperplasia is covered under health insurance. Most of the time, the insurer will cover a particular amount for the surgery. However, the amount of coverage depends on the type of policy. It is essential to know that treatments other than surgical treatments will not be covered under the health insurance.
Your insurance plan may cover all or a portion of the costs associated with the treatment of endometrial hyperplasia, including medication, surgical fees, and diagnostic tests. However, you may be responsible for co-payments or deductibles, and some treatments may require pre-authorization from your insurance provider before they will cover the costs.
To ensure that you understand your insurance coverage for endometrial hyperplasia treatment, it's important to speak with your insurance provider directly or to consult with a healthcare professional who can help you navigate the insurance process.

Know more about Endometrial Hyperplasia
Endometrial hyperplasia is a condition in which the lining of the uterus (the endometrium) becomes thicker than normal due to an excess of estrogen in the body. This can occur in women of all ages but is most common in women who are approaching menopause or who have already gone through menopause.
Glamyo Health is a healthcare brand operating in the fields of elective and cosmetic surgeries, with a chain of hospitals and clinics operating in 40+ cities all over India.
If you are looking for effective treatment for endometrial hyperplasia then consult experts at Glamyo Health. They provide the best and safest options for treatment. Know the best Gynecologist and surgeons in Delhi and Gynecology clinics. Read about the Advanced surgical options available to get vaginal tightening. We provide you with our happy patient reviews to know their journey throughout the treatment.
Causes of Endometrial Hyperplasia
Endometrial hyperplasia is caused by an imbalance of hormones in the body, specifically an excess of estrogen. This can occur for a number of reasons, including:
- Menopause: As women approach menopause, their bodies produce less progesterone, which can lead to an imbalance of hormones and an excess of estrogen.
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS): PCOS is a hormonal disorder that can cause an excess of estrogen in the body.
- Obesity: Fat cells produce estrogen, so women who are overweight or obese may have an excess of estrogen in their bodies.
- Hormonal Imbalances: Women who have hormonal imbalances, such as those caused by thyroid disorders or certain medications, may also be at risk for endometrial hyperplasia.
Symptoms of Endometrial Hyperplasia
Endometrial hyperplasia may not cause any symptoms in its early stages. However, as the condition progresses, women may experience the following symptoms:
- Abnormal Uterine Bleeding: This can include heavy or prolonged periods, bleeding between periods, or bleeding after menopause.
- Pelvic Pain: Some women may experience cramping or discomfort in the lower abdomen
- Infertility: Endometrial hyperplasia can make it difficult for women to become pregnant.
Diagnosis of Endometrial Hyperplasia
Endometrial hyperplasia is diagnosed through a biopsy of the endometrium, which involves taking a small sample of tissue from the lining of the uterus and examining it under a microscope. Additional tests may be done to rule out other conditions, such as uterine fibroids or endometrial cancer.
 New Delhi
New Delhi  Bangalore
Bangalore  Mumbai
Mumbai  Hyderabad
Hyderabad  Pune
Pune  Chennai
Chennai 
