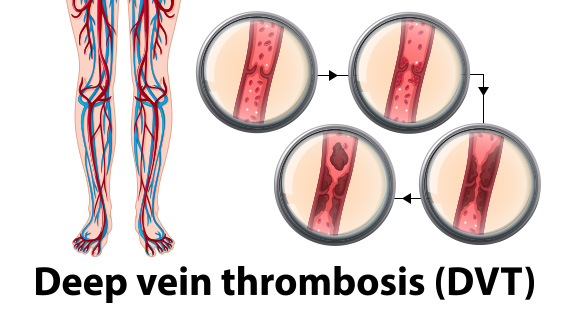
Deep Vein Thrombosis: Meaning, Symptoms, Causes & Treatment
Deep vein thrombosis refers to the medical condition in which there is clotting of blood in veins. This condition is common in old age people who are overweight, who smoke regularly, or people with some heart problems. Most important symptom of deep vein thrombosis is blood pooling in legs due to insufficient blood circulation as the valves in veins get weak.

WHAT IS DEEP-VEIN THROMBOSIS
DVT is the abbreviated form of deep vein thrombosis, which implies that veins are blocked and the blood supply to the heart is becoming difficult. Deep Veins are the vessels or tubes that help in transportation of de-oxygenated or blue blood from tissues of all the body organs towards the heart. Thrombosis is the medical term which means blood clotting in blood carrying vessels (arteries or veins).
CAUSES
- Vein injuries
- Infections
- Sedantry lifestyle
- Genetic condition
- Vein damage due to surgery
- Cancer
- Obesity
- Autoimmune disease
- Hormonal therapy
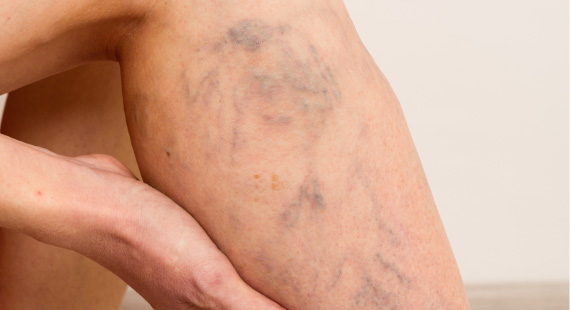
SYMPTOMS
- Swelling in your legs
- Venous stasis ulcers (ulcers on legs)
- Legs discoloration or skin pigmentation
- Blood pooling in legs
DIAGNOSIS
- Physical examination of edema in legs
- Ultrasound scan
- Venogram- X-ray of veins
- Coagulation profiles
- D-dimers
Ultrasound scan-
Complete duplex ultrasound or Proximal leg vein ultrasound
Venous ultrasound is used to check that the blood flowing in veins is not stopping or back flowing
Venogram- It is the X-ray imaging of veins to check for blood pooling.
DO's
DONT's
TREATMENTS
NON SURGICAL TREATMENTS

- Anticoagulation therapy - fondaparinux (gold standard treatment for DVT )
- Thrombolysis
- Compression hosiery
- Filters for Inferior vena cava
- Rivaroxaban
- Dabigatran
Risk and Complications
Risks associated with developing deep venous thrombosis are as follows:
- Internal blood pressure in veins is increased due to blocked veins
- If the flow of blood is reduced due to some habits or anaemic conditions
- Trauma, or venous catheter implants cause disturbance in venous flow of blood
- Highly viscous blood cause difficulties in flowing.
- Blood clotting can also be caused due to some anatomical differences in the structure of veins.
Other risk factors that lead to blood coagulation include genetic factor and acquired health problems like:
- Heart related diseases
- Inflammatory diseases
- Myocardial infarction
- Inflammatory bowel disease
- Systemic lupus erythematosus
- Cancers
COMPLICATIONS
Treatments for deep vein thrombosis can pose several complications, some of these are given below:
- Post-thrombotic syndrome
- Pulmonary emboli
- Bleeding due to anticoagulants
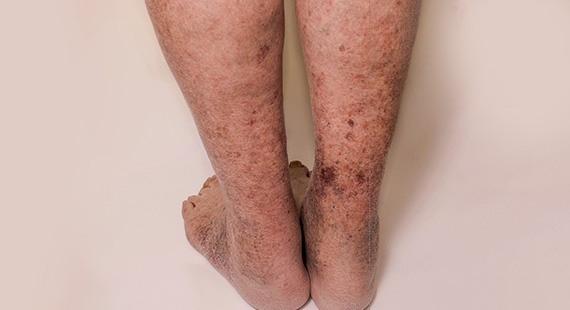
IF LEFT UNTREATED
In most of the cases, the untreated deep vein thrombosis may develop into pulmonary embolism. It is a serious health problem causing breathlessness and chest pain.
COST
The average cost of treating deep vein thrombosis is ₹20,000 - ₹30,000. The cost varies from the type of surgical procedure, hospital facilities and cities.
Financial Options

INSURANCE COVERAGE
The cost of surgical treatment for deep vein thrombosis is covered under health insurance. Most of the time, the insurer will cover a particular amount for the surgery. However, the amount of coverage depends on the type of policy. It is essential to know that treatments other than surgical treatments will not be covered under the health insurance.

Know more about Deep vein thrombosis
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a condition that occurs when a blood clot forms in a deep vein, usually in the legs. It is a serious condition that can lead to complications such as pulmonary embolism (PE), a potentially life-threatening condition in which the blood clot travels to the lungs and blocks the blood flow.
Prevention of DVT involves maintaining a healthy weight, staying active, avoiding prolonged periods of sitting or standing, and wearing compression stockings. For those who are at high risk for DVT, prophylactic measures such as the use of anticoagulants may be recommended before and after surgery or during periods of prolonged immobility.
It is important to be aware of the risk factors for DVT and to seek medical attention if you experience symptoms such as swelling, pain, or tenderness in the legs.
 New Delhi
New Delhi  Bangalore
Bangalore  Mumbai
Mumbai  Hyderabad
Hyderabad  Pune
Pune  Chennai
Chennai 
